In the ever-evolving landscape of geopolitics, the concept of a nation’s age can be both fascinating and complex. While some countries have emerged recently, others have withstood the test of time, enduring through millennia of history, wars, and cultural shifts. In this article, we’ll delve deep into the ten oldest countries as of 2024, offering insights into their rich histories and the secrets of their longevity.
Concept of a Country’s Age
According to World Population Review, the definition of a country has evolved over time. Ancient city-states like Athens and Rome were powerhouses in their era, but they weren’t countries in the modern sense. Empires that spanned vast territories, like the Roman Empire or the Han Dynasty, were also not considered individual countries. Today’s nations often emerged from the remnants of these vast empires.
Modern Birth of Nations
In recent times, countries have been born out of political upheavals, secessions, and the dissolution of larger entities. A prime example is the fragmentation of the U.S.S.R. into multiple independent nations in the late 20th century.
Determining a Country’s Birthday
The task of pinpointing a country’s exact age can be challenging.As I read on Cambridge Press, Egypt’s modern independence was recognized in 1922, its history dates back to ancient pharaohs around 3100 BCE. Similarly, China’s long history of dynasties makes its exact “birthday” a topic of debate among historians.
| Country | Sovereignty Acquired |
|---|---|
| Iran | 3200 BC |
| Egypt | 3100 BC |
| Vietnam | 2879 BC |
| Armenia | 2492 BC |
| North Korea | 2333 BC |
| India | 2000 BC |
| Israel | 1300 BC |
| Georgia | 1300 BC |
| Sudan | 1070 BC |
| Afghanistan | 678 BC |
| Mongolia | 209 BC |
| Ethiopia | 200 BC |
| Somalia | 200 BC |
| San Marino | 301 |
| Japan | 400 |
Ancient Nations in 2024 (By Date of Earliest Known Organized Government).
16. Scythia (Ukraine/Russia): 800-300 BC 🇺🇦🇷🇺
The Scythians were a group of ancient nomadic warriors who roamed the Eurasian steppes.
Historical Significance
The Scythians, mentioned by ancient historians like Herodotus, dominated vast territories from the Black Sea to China in the 1st millennium BC.
Discoveries and Attractions
Scythian burial mounds, known as kurgans, are scattered across the Eurasian steppes. The gold artifacts found in these tombs, now displayed in museums like the Hermitage in St. Petersburg, showcase the Scythians’ exquisite craftsmanship.
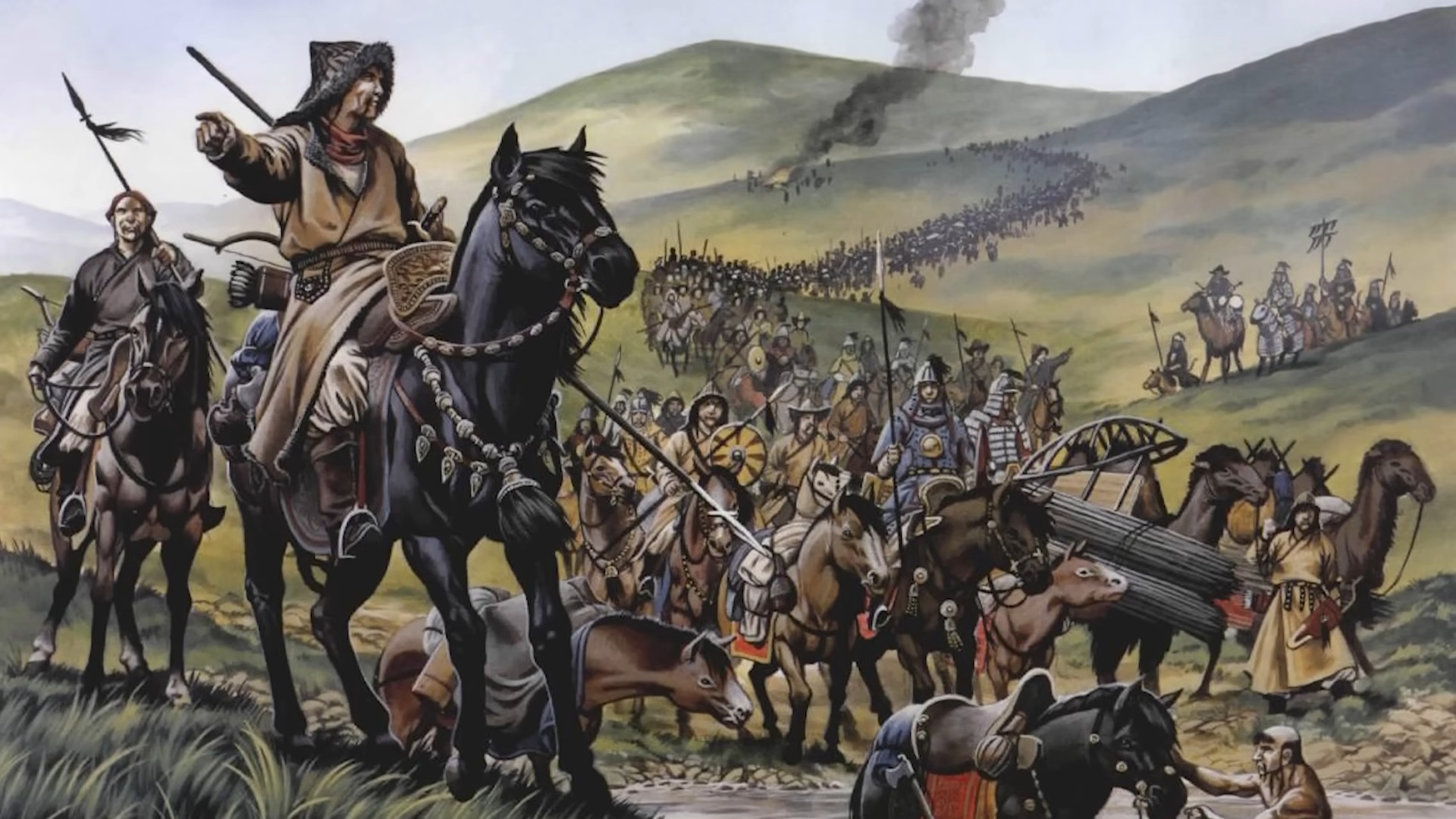
15. Mongolia: 209 BC 🇲🇳
Mongolia, known for its vast steppes and nomadic heritage, has played a significant role in Asian history.
Historical Significance
The Xiongnu Confederation, as described in Chinese historical texts, was an early nomadic empire in Mongolia. However, the region is best known for the Mongol Empire under Genghis Khan, which became the largest contiguous empire in history.
Discoveries and Attractions
The capital, Ulaanbaatar, houses the National Museum of Mongolia, which offers insights into the nation’s history. The Gobi Desert, with its unique landscapes and dinosaur fossils, is a major attraction. The annual Naadam Festival showcases traditional Mongolian sports like wrestling, archery, and horse racing.
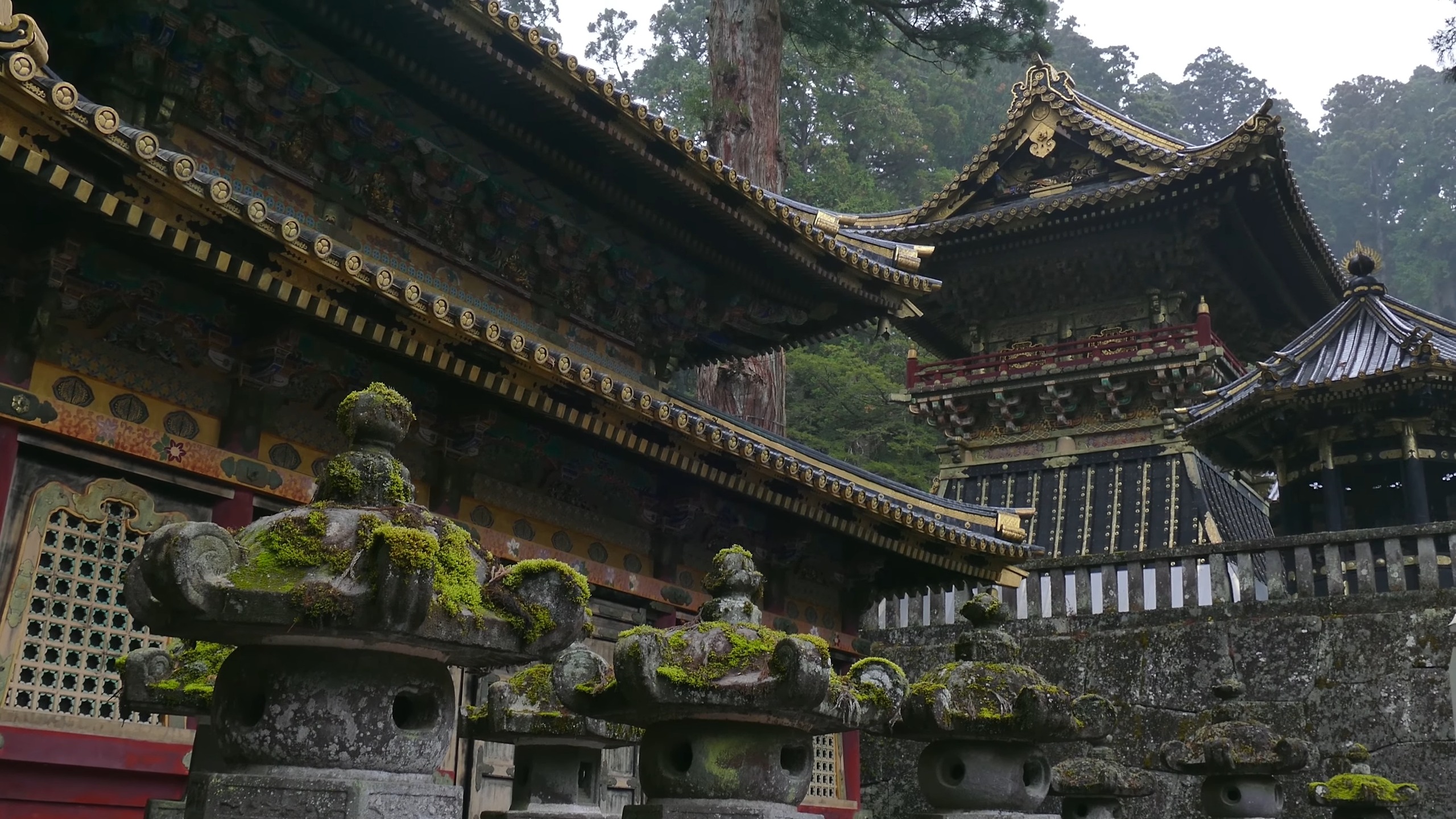
14. Japan: 660 BC 🇯🇵
Japan, the Land of the Rising Sun, is an archipelago that seamlessly blends ancient traditions with modern innovation.
Historical Significance
According to the study of the Brill, the legendary Emperor Jimmu’s ascension to the throne in 660 BC is traditionally considered the founding of Japan, marking the beginning of its imperial lineage.
Discoveries and Attractions
Kyoto, the ancient capital, is home to stunning temples and traditional tea houses. Hiroshima, with its Peace Memorial Park, serves as a poignant reminder of the horrors of war. Mount Fuji, Japan’s iconic volcano, is a popular destination for both pilgrims and tourists.
13. Afghanistan: 678 BC 🇦🇫
Afghanistan, often called the ‘Heart of Asia’, has been a melting pot of cultures due to its strategic location on the Silk Road.
Historical Significance
According to the Cambridge Press, the region has seen the rise and fall of empires, from the Medians and Achaemenids to the Mauryas and Kushans.
Discoveries and Attractions
The Bamiyan Buddhas, though sadly destroyed, remain a symbol of Afghanistan’s rich Buddhist heritage. The Minaret of Jam, a UNESCO World Heritage site, stands as a testament to the country’s architectural and cultural history.
12. Macedonia (North Macedonia): 808-146 BC 🇲🇰
Macedonia, located in the northern part of ancient Greece, rose to prominence under the leadership of King Philip II and his son, Alexander the Great.
Historical Significance
Under Alexander the Great, Macedonia expanded its territories, creating one of the largest empires in history, stretching from Greece to Egypt and as far east as India.
Discoveries and Attractions
The ancient city of Pella, the birthplace of Alexander the Great, contains well-preserved mosaics and ruins. The tomb of King Philip II in Vergina is another significant archaeological site.
11. Sudan: 1070 BC 🇸🇩
Sudan, with its vast deserts and the mighty Nile, has been home to powerful kingdoms and civilizations.
Historical Significance
As Smithsonian Magazine says, the ancient Kingdom of Kush, with its capital at Meroë, played a pivotal role in the region’s history, often interacting with ancient Egypt.
Discoveries and Attractions
The pyramids of Meroë, lesser-known than their Egyptian counterparts, offer a unique insight into the Kushite civilization. The ancient temples of Soleb and the remnants of the city of Kerma are windows into Sudan’s rich past.
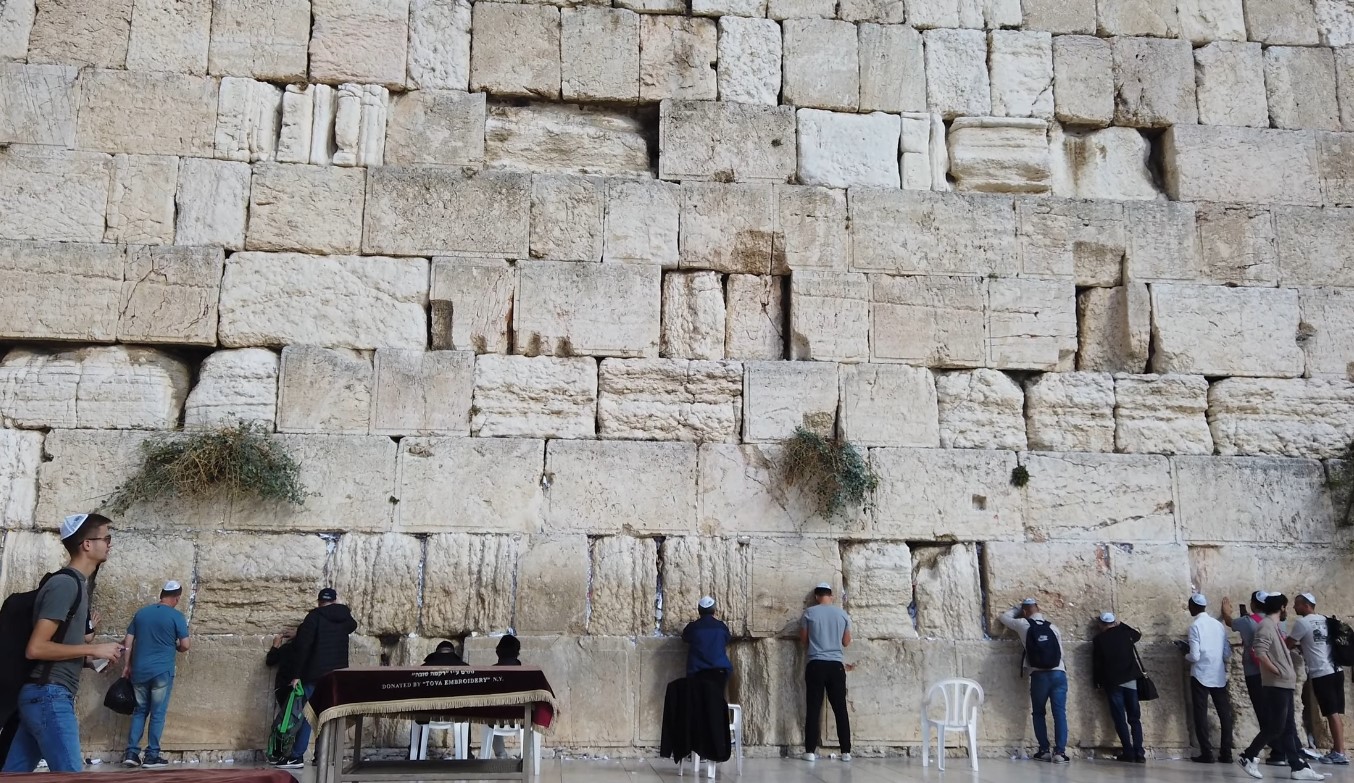
10. Israel: 1300 BC 🇮🇱
Israel, the birthplace of three major world religions, has been a crossroads of civilizations for millennia.
Historical Significance
In study conducted by JSTOR, the period of the Judges, as mentioned in the Hebrew Bible, marks a significant phase in the early history of ancient Israel.
Discoveries and Attractions
The ancient city of Jerusalem, sacred to Jews, Christians, and Muslims, is a tapestry of religious and historical sites. The Dead Sea, with its therapeutic properties, and Masada, a symbol of Jewish resistance, are among the must-visit destinations in Israel.
9. Georgia: 1300 BC 🇬🇪
Georgia, a gem in the Caucasus region, boasts a unique culture that seamlessly blends Asian and European influences.
Historical Significance
According to the Fitzwilliam Museum, the ancient kingdom of Colchis, famously associated with the Golden Fleece in Greek mythology, is among the earliest recorded civilizations in Georgia.
Discoveries and Attractions
The Uplistsikhe cave town, carved into rocky cliffs, offers a journey through Georgia’s ancient history. The vineyards of Kakheti, believed to be one of the oldest wine-producing regions in the world, invite visitors to savor the rich flavors of Georgian wine
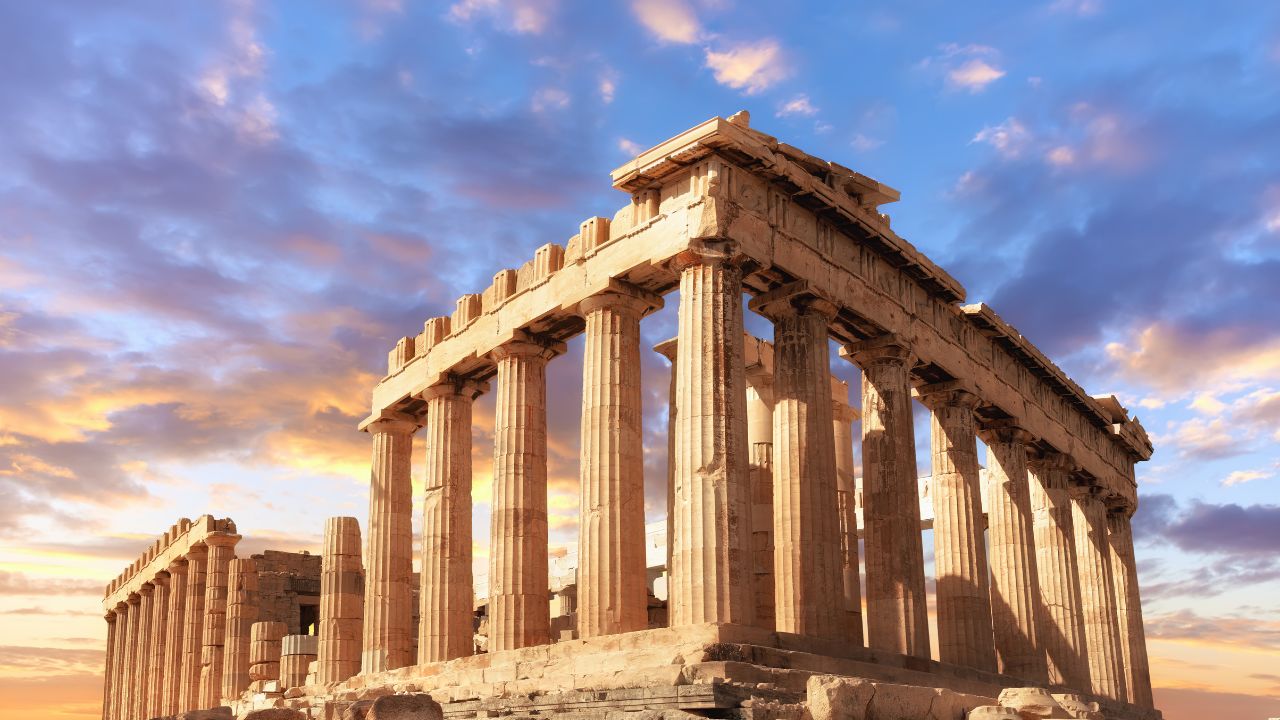
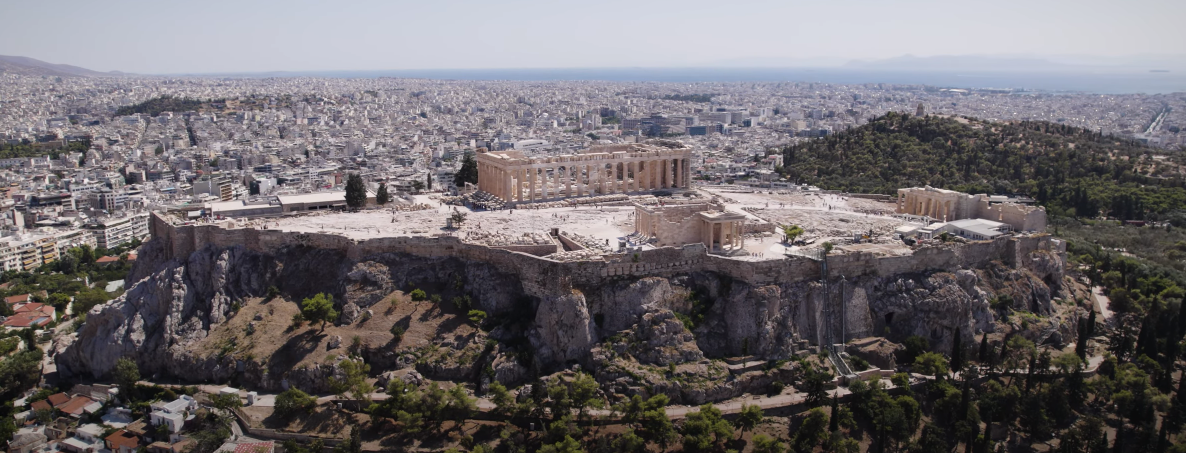
8. Greece: 1600 BC 🇬🇷
Greece, the cradle of Western civilization, has given the world democracy, philosophy, and epic tales of gods and heroes.
Historical Significance
According to the National Geographic website, the Minoan civilization on the island of Crete is among the earliest in Greece, with the Mycenaean civilization that followed laying the groundwork for classical Greek culture.
Discoveries and Attractions
The Acropolis in Athens, a symbol of ancient Greek glory, offers panoramic views of the city. The ruins of Knossos in Crete provide insights into Minoan life. Delphi, once considered the center of the world in ancient Greek religion, remains a significant archaeological site.
7. India: 2000 BC 🇮🇳
India, often referred to as the subcontinent, is a mosaic of cultures, languages, and traditions that have evolved over thousands of years.
Historical Significance
Indus Valley Civilization, one of the world’s oldest urban cultures, marked the beginning of India’s rich history.
Discoveries and Attractions
The ancient city of Varanasi, believed to be among the oldest continuously inhabited cities in the world, is a spiritual haven. The Ajanta and Ellora caves, with their intricate carvings, showcase the zenith of ancient Indian art. The Taj Mahal, a symbol of eternal love, stands as a testament to India’s architectural prowess.
6. China: 2070 BC 🇨🇳
China, with its vast landscapes and diverse cultures, has been a dominant force in East Asia for millennia.
Historical Significance
Xia Dynasty, though shrouded in myth, is often considered the first dynasty in Chinese history, laying the foundation for a series of powerful dynasties that followed.
Discoveries and Attractions
The Great Wall of China, stretching over 13,000 miles, stands as a symbol of China’s historical might. The Terracotta Army in Xi’an offers a glimpse into the grandeur of the Qin Dynasty. The Forbidden City in Beijing, once the imperial palace, showcases the zenith of Chinese architecture and culture.
5. North Korea: 2333 BC 🇰🇵
North Korea, with its enigmatic presence in modern geopolitics, has roots that trace back to ancient Korean kingdoms.
Historical Significance
As Korea.net says, the legendary Dangun founded the ancient Korean state of Gojoseon, marking the beginning of Korean history.
Discoveries and Attractions
The ancient tombs of the Koguryo Kingdom, a UNESCO World Heritage site, offer insights into early Korean art and architecture. The capital, Pyongyang, houses monuments and museums that showcase the nation’s history and culture.
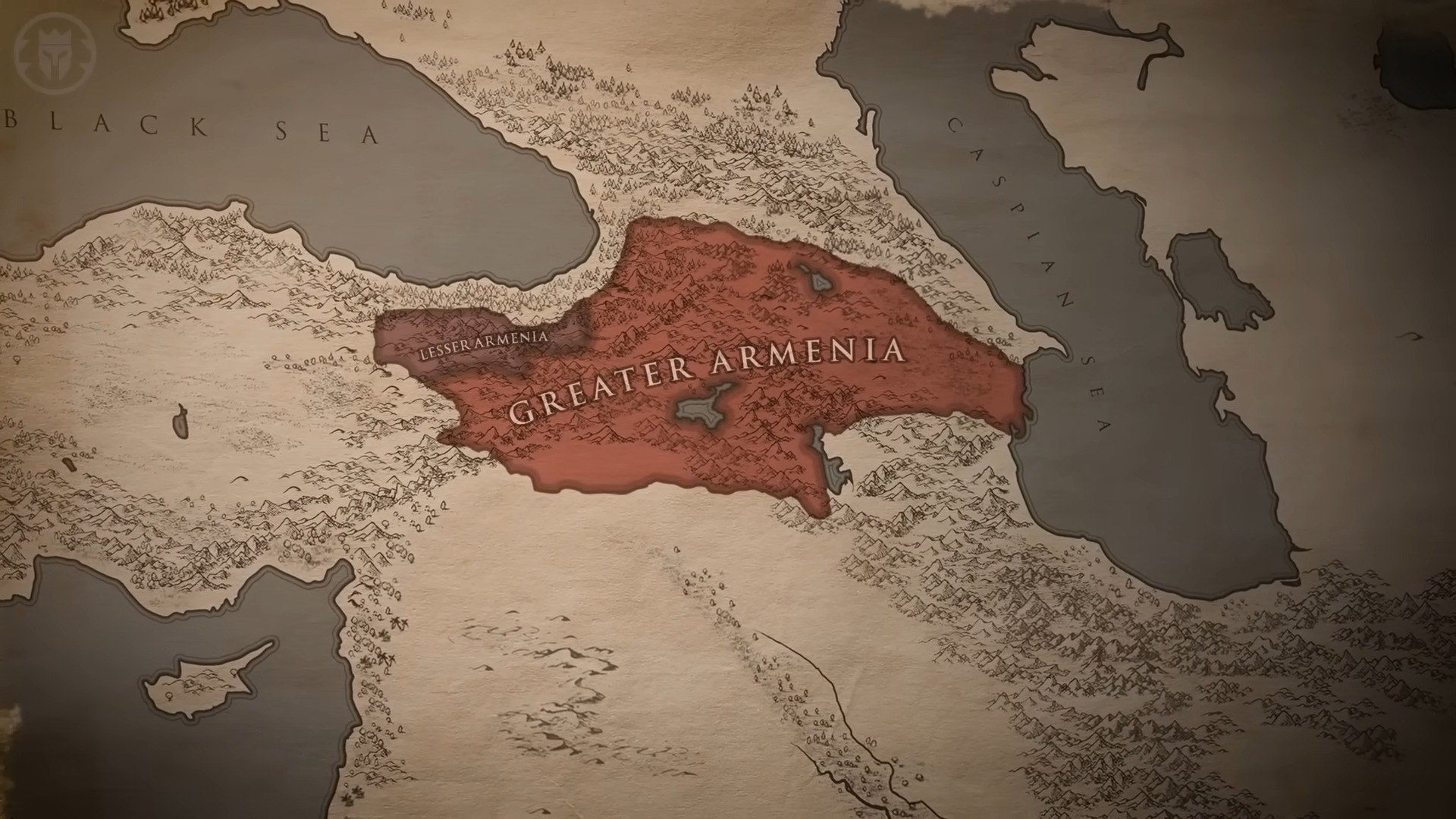
4. Armenia: 2492 BC 🇦🇲
Armenia, a nation nestled in the South Caucasus region, has a history that predates the Bronze Age.
Historical Significance
The establishment of the Nairi confederation is among the earliest recorded events in Armenian history.
Discoveries and Attractions
The ancient temple of Garni and the monastic complex of Geghard are must-visit sites. The capital, Yerevan, one of the world’s oldest continuously inhabited cities, offers a blend of the ancient and the modern.
3. Vietnam: 2879 BC 🇻🇳
Vietnam’s history is a saga of resilience, from ancient civilizations to its modern-day vibrancy.
Historical Significance
In article written by Medium we see that the Hồng Bàng dynasty, founded by the legendary Kinh Dương Vương, marks the beginning of Vietnam’s recorded history.
Discoveries and Attractions
The ancient town of Hội An, a UNESCO World Heritage site, offers a glimpse into Vietnam’s rich cultural heritage. The Imperial City in Huế showcases the grandeur of the Nguyễn Dynasty.
2. Egypt: 3100 BC 🇪🇬
Egypt, the cradle of civilization, is synonymous with its majestic pyramids, pharaohs, and the Nile River.
Historical Significance
The unification of Upper and Lower Egypt by Pharaoh Narmer marked the beginning of the First Dynasty and the rise of ancient Egyptian civilization.
Discoveries and Attractions
From the Great Pyramid of Giza to the temples of Luxor, Egypt offers a journey through time. The Egyptian Museum in Cairo houses a vast collection of ancient artifacts, including the treasures of Tutankhamun.
1. Iran: 3200 BC 🇮🇷
Iran, formerly known as Persia, boasts a rich tapestry of history that intertwines with the very roots of human civilization.
Historical Significance
According to Getty.edu, the ancient Elamite kingdoms were among the earliest civilizations in Iran. Over time, powerful empires like the Achaemenid, Parthian, and Sassanian shaped the region’s history.
Discoveries and Attractions
Visitors to Iran can explore the ruins of Persepolis, the ceremonial capital of the Achaemenid Empire, or marvel at the architectural wonders of Isfahan, once one of the largest cities in the world.
Oldest Countries in the World (By Date of Self-Sovereignty)
- Japan – 660 BCE
- China – 221 BCE
- San Marino – 301 CE
- France – 843
- Austria – 976
- Denmark – 10th century
- Hungary – 1001
- Portugal – 1143
- Mongolia – 1206
- Thailand – 1238
5 Youngest Countries in the World
- South Sudan – 2011-07-09
- Kosovo (still awaiting full recognition) – 2008-02-17
- Serbia – 2006-07-05
- Montenegro – 2006-06-03
- East Timor – 2002-05-20
While the ancient nations have tales that span millennia, the youngest countries in the world have stories of recent struggles, resilience, and rebirth. These nations, born out of political upheavals, wars, and decolonization, represent the ever-changing nature of our global landscape. Let’s delve into the histories and significance of the ten youngest countries as of 2021.
1. South Sudan: 2011-07-09 🇸🇸
South Sudan, located in East-Central Africa, became the world’s newest nation after gaining independence from Sudan.
Historical Significance
According to the Carter Center study, decades of civil wars and conflicts with Sudan culminated in a 2011 referendum where the majority voted for independence.
Discoveries and Attractions
The Sudd, one of the world’s largest wetlands, and the Boma National Park, teeming with wildlife, showcase the country’s natural beauty.
2. Kosovo: 2008-02-17 🇽🇰
Kosovo, in the Balkan Peninsula, declared independence from Serbia, though its recognition remains a contentious issue.
3. Serbia: 2006-07-05 🇷🇸
Serbia, in Southeast Europe, became an independent nation following the dissolution of the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro.
Historical Significance
The breakup of Yugoslavia in the 1990s set the stage for Serbia’s eventual independence.
Discoveries and Attractions
Belgrade, with its vibrant nightlife and historic architecture, and the stunning Tara National Park, are must-visit destinations.
4. Montenegro: 2006-06-03 🇲🇪
Montenegro, a picturesque country on the Adriatic coast, declared independence from the State Union of Serbia and Montenegro.
Historical Significance
Montenegro’s quest for autonomy can be traced back to its history as a sovereign state before joining the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats, and Slovenes in 1918.
Discoveries and Attractions
The Bay of Kotor, with its stunning fjord-like landscapes, and the medieval town of Budva, are popular among tourists.
5. East Timor: 2002-05-20 🇹🇱
East Timor, or Timor-Leste, located in Southeast Asia, gained independence from Indonesia after decades of struggle.
Historical Significance
East Timor’s journey to independence was marked by years of conflict, culminating in a UN-sponsored referendum in 1999.
Discoveries and Attractions
The Atauro Island, with its pristine beaches, and the capital city of Dili, with its blend of Portuguese and Timorese cultures, are highlights for visitors.
FAQ
What country is the oldest?
Both Iran (Persia) and Egypt are frequently cited as the world’s oldest countries due to their ancient civilizations.
Is Japan older than China?
While both have ancient histories, China’s recorded civilization predates Japan’s. The first Chinese dynasties date back thousands of years, while Japan’s recorded history starts a bit later.
Is China older than Greece?
China’s recorded history begins earlier than that of Greece. The earliest Chinese dynasties date back to around 2070 BCE, while ancient Greece’s history starts around the 8th century BCE.
What is the oldest country in Europe?
San Marino claims to be the oldest sovereign state in Europe, having been founded in 301 AD. Greece, with its ancient city-states, is the oldest civilization in Europe.
Is Iran older than Egypt?
Both countries have ancient civilizations, but Egypt’s Pharaonic period predates Iran’s earliest known dynasties. However, both are among the world’s oldest civilizations.
Which civilization is oldest?
The Sumerian civilization in Mesopotamia is often considered the world’s oldest civilization, dating back to around 3500 BCE.
What’s the youngest country?
As of 2021, South Sudan is the youngest country, having gained independence in 2011.
Is Kosovo a country now?
Kosovo declared independence from Serbia in 2008. While many nations recognize its sovereignty, some, including Serbia, do not.
What is the newest country in Europe?
Kosovo, having declared independence in 2008, is the newest country in Europe, though its recognition is still a matter of international debate.
What is the youngest state in Europe?
In terms of recognized sovereignty, Montenegro, which became independent in 2006, is among the youngest states in Europe.
Final Words
The tapestry of our world is constantly evolving, with nations old and new weaving stories of resilience, identity, and hope. As we reflect on the oldest and youngest countries, we’re reminded of the enduring spirit of humanity and the timeless quest for freedom and self-determination.
References:
- World Population Review
A source that discusses the evolving definition of a country and its historical context. - Cambridge Press
An article that delves into the challenges of determining a country’s exact age, with specific references to Egypt and China. - Brill
A study that discusses the legendary Emperor Jimmu’s ascension to the throne and its significance in Japan’s history. - Cambridge Press (Afghanistan)
A source that highlights the historical significance of the region of Afghanistan and its various empires. - Smithsonian Magazine
An article that talks about the ancient Kingdom of Kush in Sudan and its interactions with ancient Egypt. - JSTOR
A study that discusses the period of the Judges in ancient Israel as mentioned in the Hebrew Bible. - Fitzwilliam Museum
A source that mentions the ancient kingdom of Colchis in Georgia and its association with Greek mythology. - National Geographic
An article that discusses the earliest civilizations in Greece, including the Minoan and Mycenaean civilizations. - Medium (Vietnam)
An article that discusses the Hồng Bàng dynasty in Vietnam and its significance in the country’s history. - Getty.edu
A source that talks about the ancient Elamite kingdoms in Iran and the various empires that shaped the region’s history.