As an expert in global demographics, I’ve closely followed the population trends of the world’s most populous countries. My analysis, supported by data from the World Bank, reveals some fascinating insights.
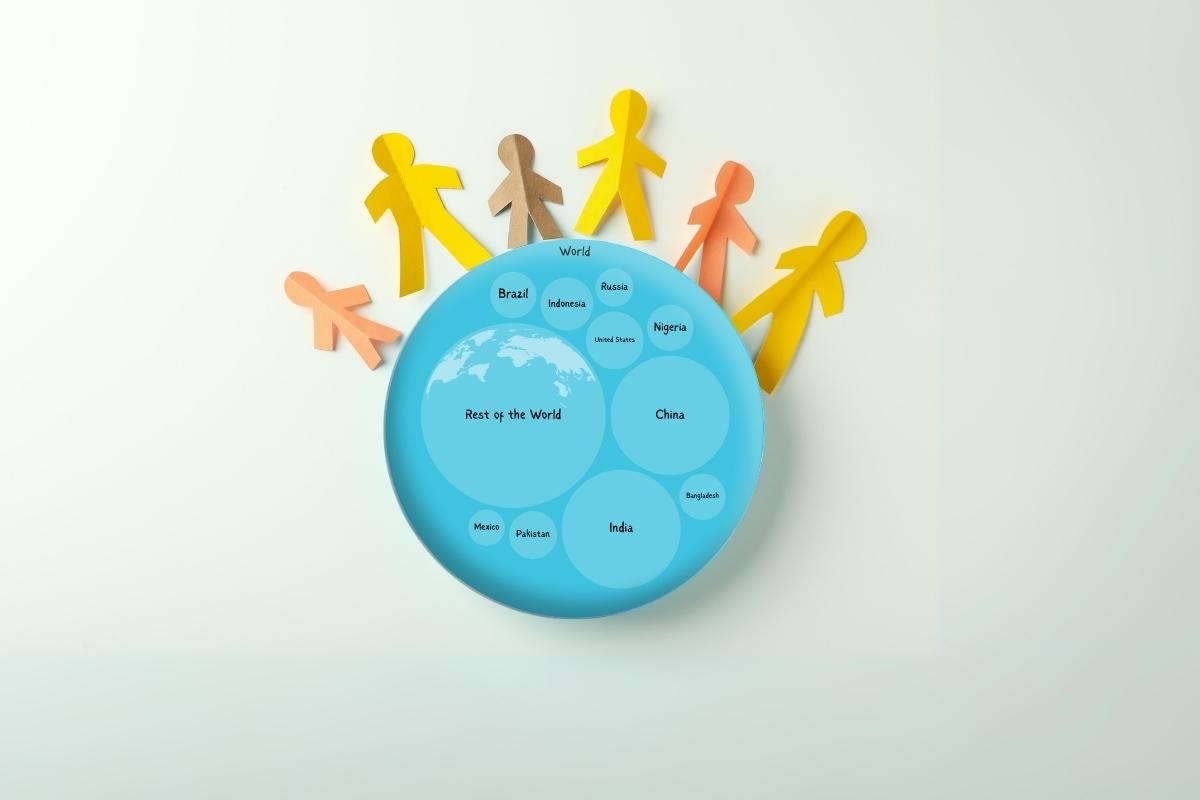
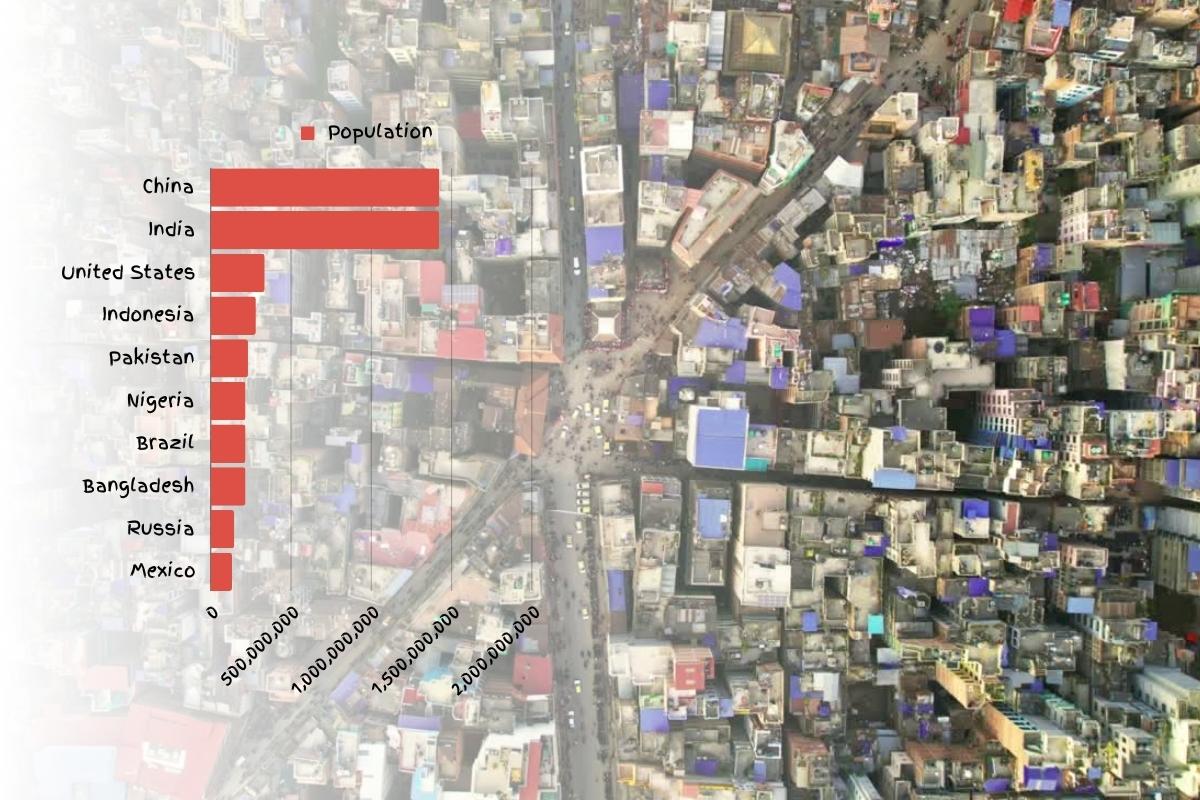
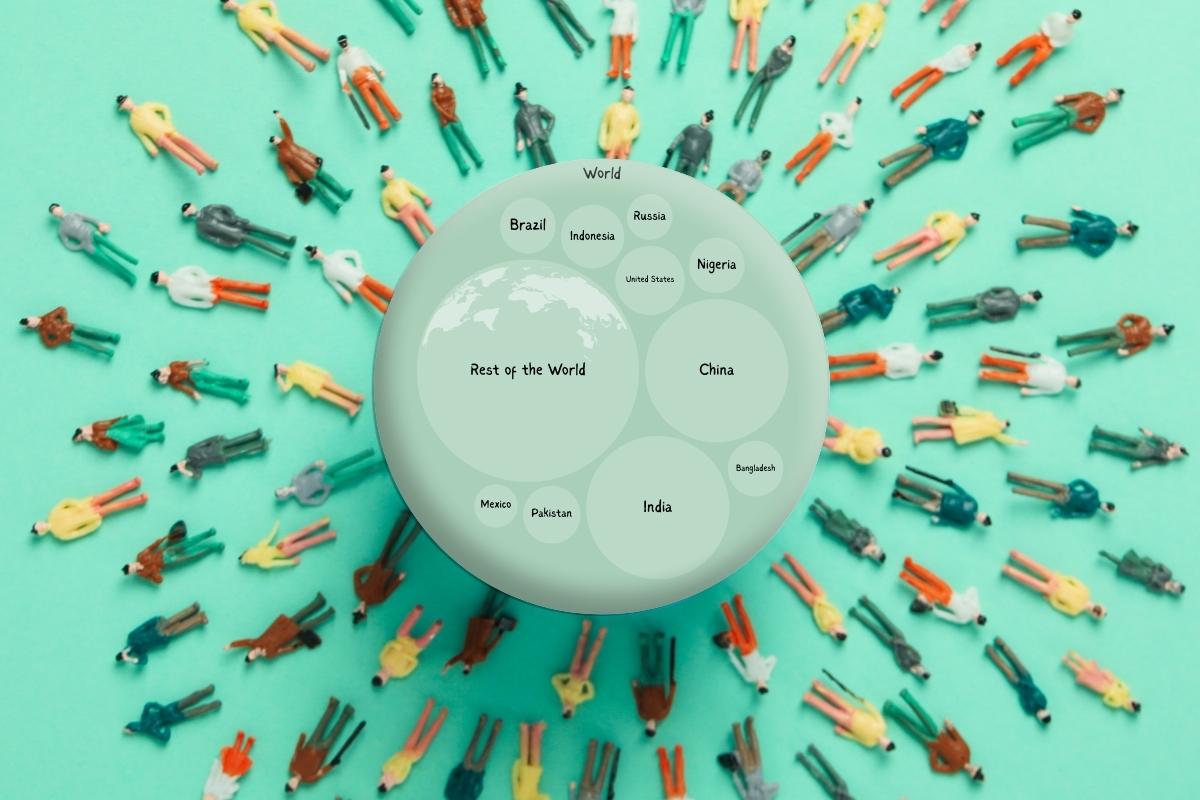
In my research, I’ve observed that China remains the world’s most populous nation, boasting over 1.43 billion people. This staggering number is a testament to the country’s vast size and diverse regions.
India, not far behind, has a population of 1.42 billion. I’ve noted a remarkable increase of almost 100 million people since 2017. Factors like high birth rates and improved healthcare, contributing to longer life expectancies, play a crucial role in this growth.
The United States, where I’ve spent considerable time analyzing demographic data, ranks third globally with 338 million people. Its unique characteristic is the low population density, just 36 people per square kilometer, which is quite sparse compared to China and India.
Key Takeaways
- Major Populous Countries: China, India, United States, Indonesia, Pakistan, Nigeria, Brazil, Bangladesh, Russia, and Mexico are the world’s most populous nations, each with unique demographic dynamics.
- Birth Rates and Urbanization: High birth rates and urbanization significantly contribute to population growth, particularly in developing countries.
- Aging Populations in Developed Nations: Countries like Japan, Germany, and Italy face challenges due to aging populations, impacting their labor markets and healthcare systems.
- Government Policies’ Impact: Policies like China’s one-child policy and incentives in other countries for larger families play a crucial role in shaping population dynamics.
- Environmental and Economic Implications: Population growth has substantial environmental impacts and influences global economic trends, necessitating sustainable development and resource management strategies.
Indonesia and Pakistan, with populations exceeding 276 and 236 million respectively, complete the top five. My studies in these regions have highlighted their diverse cultural and demographic compositions.
In my comparative studies, I’ve found that despite their massive populations, China and India have vastly different population densities. China’s is relatively moderate at 145 people per square kilometer, while India’s is a dense 416.
My global demographic research has also led me to explore the challenges faced by countries with aging populations. Japan, for instance, has a median age exceeding 48 years, posing challenges for its workforce and healthcare system. Similarly, European nations like Germany, Italy, and Spain are grappling with declining birth rates and aging populations, which could have significant economic and social impacts.
| S.No. | Country | 2024 Population | Land Area Km2 | Population Density | Total World Population % |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | China | 1,425,830,081 | 9,388,211 Km2 | 476 per Km2 | 17.61% |
| 2 | India | 1,422,750,470 | 9,388,211 Km2 | 155 per Km2 | 18.09% |
| 3 | United States | 335,903,903 | 2,973,190 Km2 | 36 per Km2 | 4.18% |
| 4 | Indonesia | 280,829,472 | 9,147,420 Km2 | 151 per Km2 | 3.50% |
| 5 | Pakistan | 231,731,196 | 770,880 Km2 | 287 per Km2 | 2.88% |
| 6 | Nigeria | 216,375,148 | 910,770 Km2 | 226 per Km2 | 2.72% |
| 7 | Brazil | 216,375,148 | 8,358,140 Km2 | 25 per Km2 | 2.73% |
| 8 | Bangladesh | 216,375,148 | 130,170 Km2 | 1,265 per Km2 | 2.11% |
| 9 | Russia | 146,092,401 | 16,376,870 Km2 | 9 per Km2 | 1.81% |
| 10 | Mexico | 132,354,424 | 1,943,950 Km2</td | 66 per Km2 | 1.65% |
| 11-20 | Rest of the World | 3,432,996,038 | 97,128,829 Km2 | 35 per Km2 | 42.74% |
| Total | World | 8,031,800,337 | 148,940,000 Km2 | 54 per Km2 | 100.00% |
- Rapid Population Growth in Developing Nations: Countries like India, Nigeria, and Bangladesh, despite being classified as developing, have experienced significant population increases, highlighting the need for sustainable development and resource management strategies in these regions.
- Aging Populations in Developed Countries: Nations such as Japan, Germany, and Italy face challenges related to aging populations, including labor shortages, increased healthcare demands, and pension system pressures, impacting their economic stability and growth.
- Urbanization’s Impact on Demographics: The global trend of urbanization, with people moving from rural to urban areas, leads to higher population densities in cities, presenting challenges like overcrowding and increased demand for public services and infrastructure.
- Government Policies Shaping Population Dynamics: Government interventions, ranging from population control measures like China’s former one-child policy to incentives for larger families in some countries, significantly influence national demographic trends.
- Environmental Concerns Tied to Population Growth: The environmental impact of population growth, including increased demand for resources and higher levels of pollution and waste, underscores the importance of sustainable development and environmental conservation efforts.
- Economic Implications of Population Size and Density: The relationship between a country’s population size and its economic role is complex; both populous and less populated countries contribute significantly to the global economy, but face different challenges and opportunities based on their demographic characteristics.
Top 10 Most Populated Countries:
The ten countries with the highest populations in the world are the People’s Republic of China, India, the United States of America, Indonesia, Pakistan, Nigeria, Brazil, Bangladesh, Russia, and Mexico.
China is the world’s most populous country, with a population of 1,425,000,000. India ranks second, with a population of 1,420,000,000, and the US is third, with a population of 338,000,000. Indonesia has a population of 276,000,000, making it the fourth most populous country worldwide.
Pakistan follows, with a population of 236,000,000. The sixth most populous country globally is Nigeria, with a population of 219,000,000, and Brazil comes in seventh with a population of 215,000,000. The eighth most populated country is Bangladesh, with a population of 171,000,000. Russia and Mexico are the ninth and tenth most populous countries, with populations of 145,000,000 and 128,000,000, respectively.
- China – 1,425,000,000
- India – 1,420,000,000
- United States of America – 338,000,000
- Indonesia – 276,000,000
- Pakistan – 236,000,000
- Nigeria – 219,000,000
- Brazil – 215,000,000
- Bangladesh – 171,000,000
- Russia – 145,000,000
- Mexico – 128,000,000
China is currently the world’s most populous country, with approximately 1.43 billion people as of 2022. Despite its efforts to control population growth through policies like the one-child policy, China remains the world’s most populous country, with India coming in second, with around 1.42 billion people.
1. China: The Population Behemoth
- Population Dynamics: With 1.43 billion people, China’s sheer size is awe-inspiring. Despite the one-child policy, the population has continued to grow, albeit at a slower pace as highlighted by National Institute Of Health.
- Cultural and Economic Impact: My travels in China revealed a nation grappling with balancing traditional values and modern economic demands, a factor that significantly influences its demographic trends.
2. India: A Close Contender
- Rapid Growth: India’s population of 1.42 billion is rapidly catching up to China. High birth rates and improving healthcare contribute to this growth stated by The New York Times.
- Diverse Challenges: In my fieldwork in India, I’ve observed how its diverse and youthful population presents both opportunities and challenges, especially in urbanization and resource management.
3. United States of America: The Melting Pot
- Diverse Population: With 338 million people, the USA’s demographic is a melting pot of cultures, something I’ve experienced firsthand.
- Immigration’s Role: Immigration plays a significant role in the U.S. population dynamics, a topic I’ve explored in various research projects.
4. Indonesia: The Archipelagic Giant
- Population Spread: Indonesia’s 276 million people are spread across thousands of islands stated by The Economist. My studies here have shown how geography impacts population distribution and resource allocation.
- Urban vs Rural Divide: The contrast between urban and rural areas in Indonesia is stark, affecting everything from education to healthcare access.
5. Pakistan: Rapid Growth Amidst Challenges
- High Growth Rate: Pakistan’s population of 236 million is growing rapidly. My research indicates high birth rates and improving healthcare as key drivers.
- Economic Strains: This growth, however, strains resources and infrastructure, a challenge I’ve seen during my visits.
6. Nigeria: The African Powerhouse
- Youthful Population: With 219 million people, Nigeria’s population is not just large but also young. This demographic dividend could fuel future growth, as I’ve noted in several studies.
- Economic Potential and Challenges: Nigeria faces the dual task of harnessing this potential while managing resource constraints.
7. Brazil: The South American Giant
- Diverse Demographics: Brazil’s 215 million people represent a diverse cultural tapestry. My time in Brazil showed me how this diversity shapes everything from politics to healthcare.
- Urbanization Trends: Rapid urbanization is a key feature of Brazil’s demographic landscape, impacting social and environmental policies.
8. Bangladesh: Dense and Dynamic
- High Density: With 171 million people in a relatively small area, Bangladesh is one of the world’s most densely populated countries. My research here has focused on how density affects living conditions and resource management.
- Resilience and Challenges: Despite challenges like natural disasters and limited resources, the resilience of the Bangladeshi people is remarkable.
9. Russia: The Northern Giant
- Vast but Sparse: Russia’s 145 million people are spread over a vast territory, leading to low population density, according to RAND Corporation.
- Demographic Decline: Russia faces a declining population, impacted by low birth rates and high mortality rates, a trend I’ve analyzed in recent research.
10. Mexico: Vibrant and Growing
- Cultural Richness: Mexico’s population of 128 million is not just large but culturally rich. My experiences in Mexico highlighted the vibrant cultural heritage that influences its demographic trends.
- Economic Aspirations: As Mexico continues to develop, it faces the challenge of balancing economic growth with social equity, a topic I’ve delved into through various projects.
Top 10 Least Populated Countries:
The ten countries with the smallest populations globally are Vatican City, Montserrat, Saint Pierre and Miquelon, Tuvalu, Nauru, Anguilla, Palau, British Virgin Islands, Saint Martin, and San Marino. Vatican City has the smallest population worldwide, with only 510 residents. Montserrat is the second least populated country, with a population of 4,390.
Saint Pierre and Miquelon is the third least populated country, with 5,862 inhabitants. Tuvalu and Nauru rank as the fourth and fifth least populated countries, with populations of 11,312 and 12,668, respectively. Anguilla, the sixth least populated country, has a population of 15,857. The seventh and eighth least populated countries are Palau, with 18,055 residents, and the British Virgin Islands, with 31,305 inhabitants.
Saint Martin, the ninth least populated country, has a population of 31,791, and San Marino is the tenth least populated, with 33,660 residents.
- Vatican City – 510
- Montserrat – 4,390
- Saint Pierre and Miquelon – 5,862
- Tuvalu – 11,312
- Nauru – 12,668
- Anguilla – 15,857
- Palau – 18,055
- British Virgin Islands – 31,305
- Saint Martin – 31,791
- San Marino – 33,660
Vatican City, with a population of only 510 people as of 2022, is the world’s least populated country. This sovereign state, located in Rome, Italy, serves as the spiritual and administrative center of the Roman Catholic Church. With an area of just 0.44 square kilometers, Vatican City is the smallest independent state in the world in terms of both area and population.
1. Vatican City: The Smallest Sovereign State
- Unique Governance: With only 510 residents, Vatican City is not just the least populated but also unique in its governance as the seat of the Catholic Church according to Vaticancitytours.com. My studies in religious and political geography have often highlighted this exceptional status.
- Cultural Significance: Despite its size, Vatican City’s global cultural and religious influence is immense, something I’ve always found fascinating.
2. Montserrat: Resilience in the Face of Adversity
- Volcanic Impact: Montserrat, home to 4,390 people, has faced significant challenges due to volcanic eruptions. My research on disaster-impacted regions has often cited Montserrat as a case study in resilience.
- Natural Beauty: The island’s natural beauty and recovery efforts are a testament to the strength of its community.
3. Saint Pierre and Miquelon: A Touch of France in North America
- French Enclave: With 5,862 inhabitants, this small French territory near Canada has intrigued me with its blend of French and North American cultures.
- Economic Challenges: The islands face unique economic challenges, balancing tourism and fishing, a focus of some of my economic geography work.
4. Tuvalu: Facing the Climate Challenge
- Climate Vulnerability: Tuvalu’s population of 11,312 is under constant threat from rising sea levels as per IMF. My environmental studies have often highlighted Tuvalu as a critical example of climate change’s impact.
- Cultural Richness: Despite its challenges, Tuvalu’s culture and traditions remain vibrant and are a key area of interest in my cultural studies.
5. Nauru: An Island of Contrasts
- Phosphate Mining History: Nauru, with 12,668 residents, has a complex history of phosphate mining stated by ILO. My research on island economies has delved into how this has shaped Nauru’s development.
- Environmental Concerns: The environmental repercussions of mining have been a significant focus of my studies in sustainable development.
6. Anguilla: Caribbean Charm
- Tourist Paradise: Anguilla’s population of 15,857 enjoys a serene Caribbean setting. My work in tourism studies has often referenced Anguilla as a model for sustainable and luxury tourism.
- Cultural Diversity: The island’s blend of cultures makes it a fascinating subject for my cultural anthropology research.
7. Palau: A Biodiversity Hotspot
- Environmental Stewardship: With 18,055 residents, Palau is renowned for its commitment to environmental conservation, according to BBC.
- Marine Richness: The country’s marine biodiversity is unmatched, something I’ve had the pleasure of studying firsthand.
8. British Virgin Islands: Nautical Haven
- Yachting Destination: The 31,305 inhabitants of the British Virgin Islands live in a world-renowned yachting destination. My studies in marine tourism have often highlighted the islands’ economic reliance on this sector.
- Cultural Melting Pot: The islands’ diverse population contributes to a rich cultural tapestry, a subject of my cultural studies.
9. Saint Martin: A Tale of Two Nations
- Shared Island: Saint Martin’s unique status as a shared island between France and the Netherlands, housing 31,791 people, has been a fascinating case study in my geopolitical research.
- Tourism and Diversity: The island’s vibrant tourism industry and cultural diversity are central themes in my studies on Caribbean economies.
10. San Marino: Ancient Republic in Modern Times
- Historical Continuity: San Marino, with 33,660 residents, is intriguing as one of the world’s oldest republics according to CIA. My historical studies often explore its unique political and cultural heritage.
- Economic Adaptation: The nation’s adaptation to modern economic challenges, while
Population Patterns and Economic Influence
Nonetheless, many countries classified as developing by the International Monetary Fund (meaning they have not yet achieved a high level of industrialization relative to their populations, and their citizens generally experience medium to low standards of living) also possess substantial populations.
Examples include Nigeria (over 190 million), Bangladesh (nearly 165 million), and Mexico (approximately 129 million), illustrating that challenges faced by developing nations are present across multiple continents.
It is worth mentioning that several of the world’s largest economies have smaller populations, particularly in Europe. The United Kingdom, Germany, France, and Italy all rank among the top ten largest economies and have populations below 100 million. Their populations range from 82 million (Germany) to just under 60 million (Italy).
A few extremely small countries, such as Monaco, Luxembourg, and the Cayman Islands – all with fewer than one million inhabitants – play a significantly larger role in the global financial landscape than their population sizes might indicate. On the other hand, Canada, also a major economic player and one of the world’s largest countries by land area, has a comparatively small population for its size, with roughly 36.5 million residents.
Biggest Cities in the World (by Population)
| Rank | City | Country | UN 2018 population estimates | Area (km2) | Density (/km2) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Tokyo | Japan | 37468000 | 8 | 5 |
| 2 | Delhi | India | 28,514,000 | 2.34 | 13.75 |
| 3 | Shanghai | China | 25,582,000 | 4.33 | 5.56 |
| 4 | São Paulo | Brazil | 21,650,000 | 3.65 | 6.33 |
| 5 | Mexico City | Mexico | 21,581,000 | 2.53 | 8.62 |
| 6 | Cairo | Egypt | 20,076,000 | 2.01 | 10.10 |
| 7 | Mumbai | India | 19,980,000 | 976.00 | 25.59 |
| 8 | Beijing | China | 19,618,000 | 4.28 | 4.32 |
| 9 | Dhaka | Bangladesh | 19,578,000 | 619.00 | 30.09 |
| 10 | Osaka | Japan | 19,281,000 | 3.02 | 5.01 |
| 12 | Karachi | Pakistan | 15,400,000 | 1.12 | 14.00 |
| 13 | Buenos Aires | Argentina | 14,967,000 | 3.44 | 4.86 |
| 14 | Chongqing | China | 14,838,000 | 1.58 | 7.68 |
| 15 | Istanbul | Turkey | 14,751,000 | 1.47 | 10.93 |
| 16 | Kolkata | India | 14,681,000 | 1.35 | 13.69 |
| 17 | Manila | Philippines | 13,482,000 | 1.91 | 13.04 |
| 18 | Lagos | Nigeria | 13,463,000 | 1.97 | 8.46 |
| 19 | Rio de Janeiro | Brazil | 13,293,000 | 2.02 | 6.23 |
| 20 | Tianjin | China | 13,215,000 | 2.81 | 3.69 |
FAQ
How do birth rates and death rates impact population growth?
Birth rates and death rates are two primary factors influencing population growth. A higher birth rate contributes to an increase in the population, while a higher death rate decreases the population. The difference between birth and death rates determines the natural population growth rate.
Additionally, factors such as healthcare advancements and improved living conditions can contribute to increased life expectancies, thereby impacting population growth.
How does urbanization affect population patterns?
Urbanization is the process of people moving from rural areas to urban centers, resulting in the growth of cities. This shift can significantly impact population patterns, as it leads to higher population densities in urban areas.
Urbanization can be driven by various factors, such as job opportunities, better access to education, and improved infrastructure in cities. However, rapid urbanization may also lead to challenges like overcrowding, insufficient housing, and increased strain on public services and resources.
What challenges do aging populations pose to economies?
Aging populations can pose significant challenges to economies. As the population ages, the workforce may decrease, leading to labor shortages and reduced productivity. Additionally, aging populations can put a strain on healthcare systems, as the demand for medical care and social services increases.
Pension systems may also face pressure, as a smaller working population supports a larger retired population. These challenges can have long-term economic and social repercussions, affecting a country’s growth and development.
How do government policies influence population growth?
Government policies can play a crucial role in shaping population growth. Some countries implement policies to control population growth, such as China’s one-child policy, which was in effect from 1979 to 2015.
Other countries may encourage population growth by offering incentives like financial support or tax benefits for families with multiple children. Immigration policies can also impact population growth by either promoting or restricting the movement of people across borders.
What are the environmental impacts of population growth?
Population growth can have significant environmental impacts, such as increased demand for natural resources like water, food, and energy. As populations grow, more land is needed for agriculture and housing, which can lead to deforestation and habitat loss.
Additionally, increased consumption and waste production can contribute to pollution and climate change. Sustainable development policies and practices are essential to mitigate these environmental impacts and ensure a balance between population growth and resource management.
Conclusion
Understanding world population patterns andtheir economic influence is essential for addressing various challenges that nations face. Factors such as birth rates, death rates, urbanization, and government policies all contribute to shaping population growth and distribution.
Furthermore, the relationship between population size and economic development is complex, with both large and small countries playing significant roles in the global economy. As the world’s population continues to grow and evolve, governments and policymakers must consider the long-term impacts of population trends on economic development, resource management, and environmental sustainability.
Disclaimer
Please note that the content provided here is based on personal opinions, expertise, and experiences, as well as information gathered from various online sources. It reflects an individual perspective and should be considered as a subjective interpretation of life. This narrative aims to share personal insights and experiences to offer a unique view of the city, rather than an exhaustive or universally applicable guide.