Navigating through the various stages of pregnancy can be a daunting task, particularly for first-time parents. Understanding the breakdown of pregnancy into months and learning to calculate your pregnancy from weeks to months can significantly aid in grasping the changes occurring during this period. Being aware of the progression from weeks to trimesters is essential for knowing what to expect, preparing for delivery, and maintaining optimal care throughout your journey.
There are two primary methods for confirming pregnancy: an at-home urine test and a doctor-administered blood test. as highlighted in Cleveland Clinic report. If your home pregnancy test returns a positive result, it is advisable to see a doctor for confirmation, especially if you have experienced a high-risk pregnancy, such as a tubal pregnancy, in the past.
Key Takeaways
- Recognize the significance of calculating pregnancy from weeks to months and the importance of knowing each trimester for better monitoring and preparation.
- Learn about the reliability of home pregnancy tests and the necessity of doctor-administered blood tests, as recommended by health professionals, for accurate confirmation.
- Emphasize the importance of regular prenatal visits, ultrasound examinations, and holistic care, including proper nutrition and exercise, throughout the pregnancy for the health of both mother and baby.
- Gain insights into the key developmental milestones of the fetus during each trimester, aiding in understanding the growth and changes occurring within the womb.
- Acknowledge the postpartum period’s challenges, including the possibility of postpartum depression, and stress the importance of seeking medical advice and emotional support during this time.
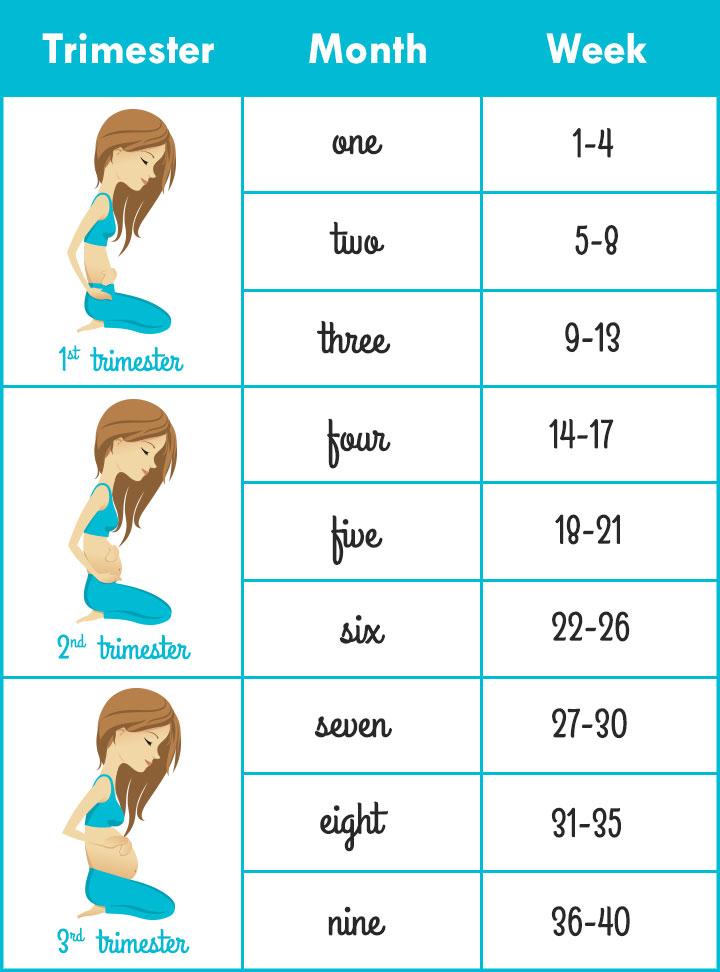
Calculating Pregnancy Weeks to Months
Pregnancy Start Time
Though it might be surprising to some, pregnancy doesn’t commence at conception. In fact, it is counted from the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP). Consequently, pregnancy duration extends to 40 weeks or 10 months.
There are several methods to assess how far along a pregnancy is:
- Last menstrual period: Calculate the number of days or weeks that have passed since the first day of the LMP.
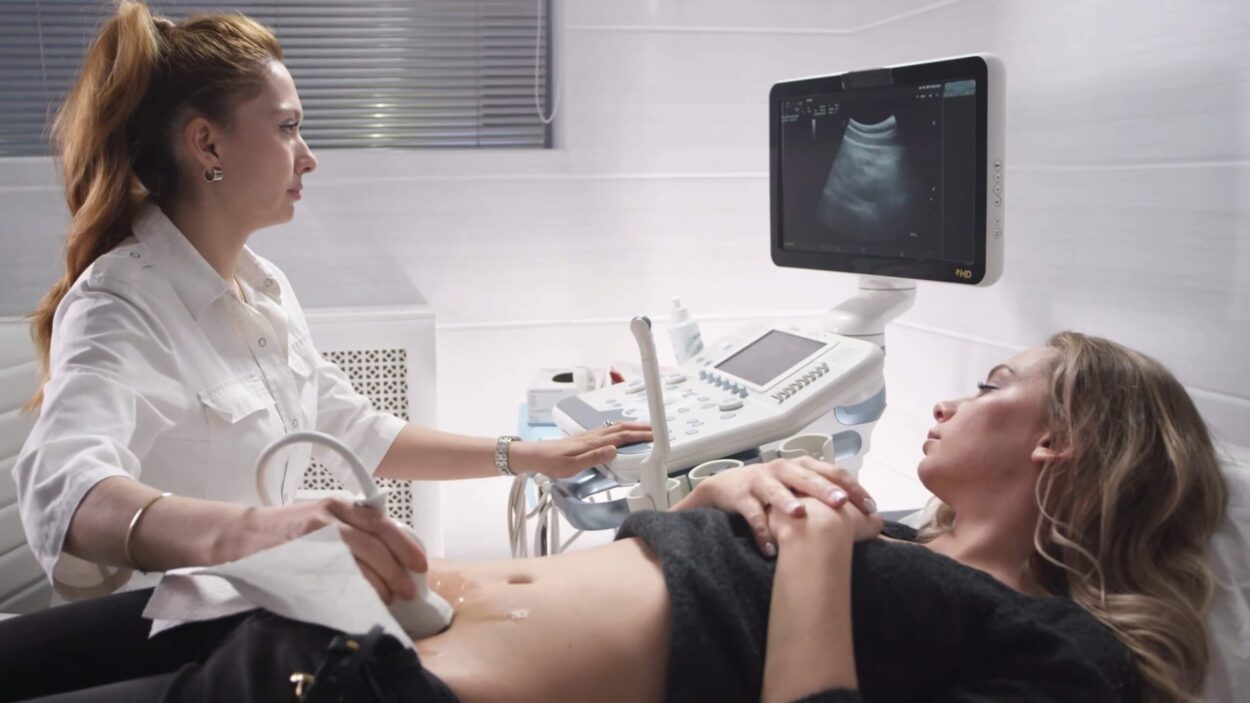
- Ultrasound examination: Undergo an ultrasound, allowing the doctor to estimate the pregnancy duration based on the embryo or fetus size.
These techniques, along with pregnancy calculators, can help in determining the weeks and months of pregnancy while understanding how trimesters fit into the overall timeline. This knowledge enables expectant parents to prepare and anticipate the changes during each stage until the baby’s arrival.
Fetal Development Stages
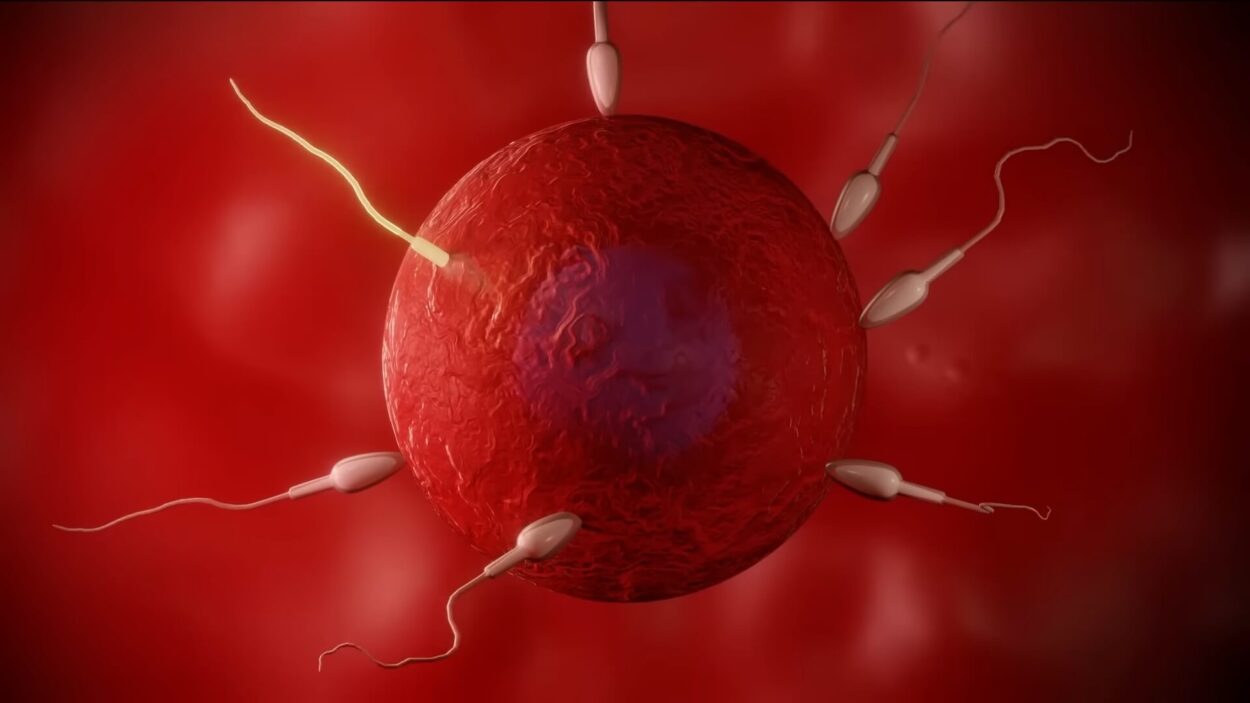
1. Germinal Stage:
- Starts: At conception in the fallopian tube.
- Process: Sperm fertilizes the egg, creating a zygote.
- Journey: Zygote moves to the uterus over about a week, dividing many times.
- Outcome: Zygote becomes a blastocyst, implants in the uterine lining, and triggers pregnancy-supporting hormones, halting the menstrual period.
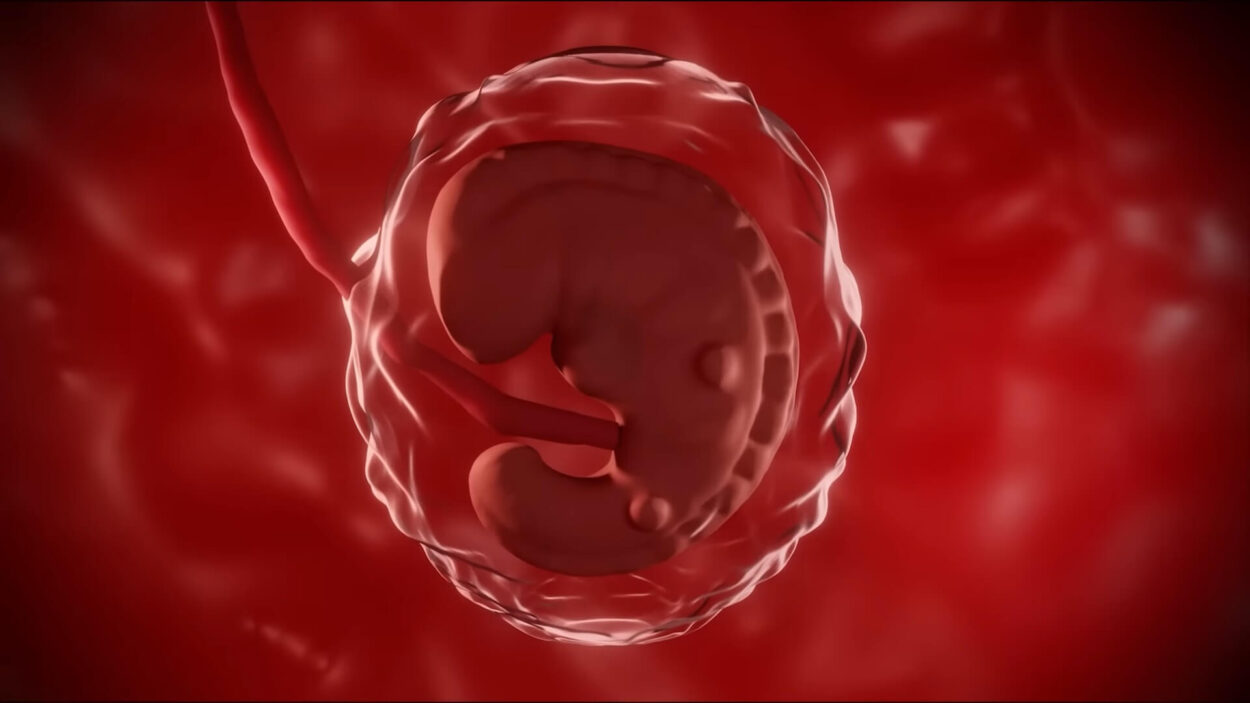
2. Embryonic Stage:
- Duration: From the third to the eighth week of pregnancy.
- Development: The blastocyst transforms into an embryo.
- Formation: Neural tube, head, eyes, mouth, limbs start forming.
- Key Milestones: Heart development and pulse around the sixth week, limb buds form.
3. Fetal Stage:
- Commencement: From the ninth week until birth.
- Transition: The embryo becomes a fetus.
- Growth: Major organs and body systems grow and mature.
- Features: Development of fingernails, eyelashes, hair; fetus moves limbs.
How Long Is Pregnancy in Weeks?
Pregnancy typically spans about 40 weeks or 280 days as noted by NCBI. These weeks are organized into three distinct trimesters:
- First trimester: Lasts for 14 weeks or 3.5 months
- Second trimester: Lasts for 14 weeks or 3.5 months
- Third trimester: Lasts for 12 weeks or 3 months
Throughout the pregnancy, various milestones in fetal development and changes in the mother’s body occur. Ultrasound examinations help track the fetus’s growth and the development of the placenta.
First Trimester in Weeks
It is essential to schedule the first prenatal visit early in the first trimester to ensure a healthy pregnancy for both the mother and baby. As weeks pass, staying informed about what to expect at each stage in the first trimester can assist in better preparation.
- Weeks 1-3: In the initial three weeks, the pregnancy is still quite young, with doctors counting back to the first day of the last period. Although not pregnant yet during the first two weeks, conception occurs after the second week. In the third week, the baby appears as a small cluster of cells.
- Weeks 4-6: At this stage, the pregnancy is approaching the two-month mark, and the baby undergoes significant changes. From being a cluster of cells, the fetus begins developing a brain, organs, a spinal cord, and skin.
- Weeks 7-9: Entering the third month of pregnancy, weeks 7 through 9 are marked by more rapid growth for the baby. The baby starts developing distinct features, including the head, nose, and limbs according to babycenter.
- Weeks 10-14: Finally reaching the end of the first trimester, the baby can now bend its limbs, produce and expel urine, and develop genitals and fingernails during these weeks.
Second Trimester: Weekly Overview
In the second trimester, running from week 14 to week 28, expectant mothers typically experience a decrease in nausea and a resurgence in their energy levels. This span of time is essential to prepare for delivery and explore various delivery methods in collaboration with your partner according to www.pregnancybirthbaby.org.au.
During the second trimester, notable milestones take place for both the mother and the baby. A brief week-by-week outline traced below depicts noteworthy developments:
- Weeks 14-15: Within these weeks, the baby establishes their hair and scalp patterns and forms stronger bones.
- Weeks 16-18: As you embark on the fourth month of pregnancy, your baby attains the ability to move their eyes, cultivate toenails, and perceive sounds. Week 18 usually offers the opportunity to learn the baby’s gender through a mid-pregnancy ultrasound as it is stated in the Parents blog article.
- Weeks 19-21: By the end of week 20, you have surpassed the halfway point of pregnancy. During this period, your baby’s movements become more noticeable according to Vinmec’s study.
- Weeks 22-24: Entering the sixth month of pregnancy, your unborn child develops hair, as well as distinct fingerprints and footprints.
- Weeks 25-28: Nearing the conclusion of the second trimester, your baby can now hear your voice, signifying another thrilling moment in pregnancy.
Third Trimester
During the third trimester, which spans from weeks 28 to 40, final preparations take place as you eagerly await your baby’s arrival. It is essential to organize everything before the big day, including knowing what to pack in your hospital bag and discussing feeding options for your baby, such as breastfeeding or bottle-feeding.
Timeline of the Weeks
- Weeks 28-30: At the beginning of this trimester, you’re around seven months pregnant. Expect your baby to grow more hair and become increasingly active through kicking and stretching.
- Weeks 31-33: As you enter your eighth month of pregnancy, your baby will have completed their major development stages and will now be rapidly gaining weight.
- Weeks 34-36: By the end of week 36, you’re nine months pregnant. Your baby will go through final developments, such as skin smoothing and nail growth.
- Weeks 37-40: You’re in the homestretch and could give birth at any moment during these final weeks of your pregnancy.
When is Delivery Considered Premature or Late?
A baby born before 37 weeks, or nine months, is considered premature. Earlier deliveries carry a higher risk of complications, and these babies may require specialized care. Babies born before 28 weeks, or seven months, face an even higher risk of lasting complications into adulthood.
When a pregnancy goes past 41 weeks, or 10 months, it is considered late. Your doctor may attempt various techniques to induce labor. If these methods fail, a cesarean delivery, or C-section, may become necessary.
Common Health Concerns for Premature or Late Babies
Premature babies born before 25 weeks often weigh one pound or less, have low body fat, and may experience breathing problems according to URMC Rochester.
Late babies face their own set of issues, with size being a primary concern. A C-section may be required if inducing labor proves unsuccessful. Other concerns for late babies include potential heart rate issues caused by stress or low amniotic fluid noted by NCBI.
What Is the Postpartum Period?
The postpartum period spans between 6 to 8 weeks following childbirth. Within this crucial time frame, the primary focus for parents is to forge a strong bond with their newborn noted in this study of NCBI. It is essential to note that instant connections with newborns are not universal for every parent, as the bonding process varies in duration for different individuals. Nonetheless, caring for and attending to a newborn’s needs will organically cultivate the special bond between parent and baby.
Unfortunately, quite a few women, approximately one in five, encounter postpartum depression during this period. Manifestations of this condition can include overwhelming sadness, anxiety, and reduced interest in the baby, among other symptoms stated by the same source in different study.
It is important to emphasize that postpartum depression is experienced differently among women, varying in severity. For those struggling with symptom management, seeking assistance from healthcare providers or therapists is highly advisable. Acknowledgment of the prevalence and treatability of these symptoms can offer solace and reassurance that help is available and that individuals facing this challenge are not isolated.
Holistic Care During Each Month of Pregnancy
You should provide comprehensive care throughout each month of pregnancy, prioritizing the well-being of both the mother and the baby. The center follows guidelines from the American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists and the World Health Organization to ensure the best possible care.
Key aspects of pregnancy management include:
- Weight Gain: The center offers a weight gain calculator to help expectant mothers maintain a healthy weight during their pregnancy.
- Exercise: Encouraging safe and appropriate physical activities tailored to each stage of pregnancy.
- Nutrition: Providing guidance on a balanced diet, including essential nutrients like folic acid and other vitamins and minerals.
- Holistic Care: Ensuring emotional and psychological support for expectant parents, in addition to physical health measures.
Frequently Asked Questions
When Can Pregnancy Be Detected?
After conception, the hormone HCG is present in your blood. This hormone, crucial for pregnancy tests, becomes detectable approximately three to four weeks from the last menstrual period.
How to Convert Weeks of Pregnancy Into Months?
There is no exact conversion as the number of weeks in a month varies. However, a commonly used conversion is to simply divide the total number of weeks by 4. For example, 20 weeks would be approximately 5 months pregnant. Keep in mind that some months have slightly more than 4 weeks.
How Many Weeks Are Equivalent to 9 Months of Pregnancy?
Typically, there are 40 weeks in a full-term pregnancy, which is roughly 9 months. However, some people might consider it as 10 months, counting 4 weeks per month.
What Is the Week Count at 7 Months of Pregnancy?
At 7 months pregnant, you are likely around 28 to 31 weeks along. To break it down further, you can consider that an average month has 4.35 weeks, so 7 months would be approximately 30.45 weeks.
When Are 5 Months of Pregnancy Completed in Terms of Weeks?
The completion of 5 months of pregnancy in weeks is around 21 to 22 weeks. This estimation is based on the average month having 4.35 weeks.
What Is the Duration of A Full-Term Pregnancy in Weeks?
A full-term pregnancy usually lasts 40 weeks, or 280 days, from the first day of the last menstrual period (LMP). Premature births occur before the 37th week, and post-term pregnancies go beyond 42 weeks.
Can We Consider 23 Weeks of Pregnancy as 6 Months?
It’s not entirely accurate to consider 23 weeks of pregnancy as 6 months, but it’s relatively close. Using the average month of 4.35 weeks, 6 months would be around 26.1 weeks pregnant. Some sources might consider 23 to 24 weeks as the beginning of the 6th month, but it’s essential to recognize that these estimates might not be exact.
Crucial Weeks for Fetal Development?
The first 13 weeks, or the first trimester, are critical for fetal development. During this phase, the risk of miscarriage decreases significantly as major organs and systems form. The importance of pregnancy care continues throughout, but the initial weeks are vital for reducing major birth disorders.
Final Words
Stages of pregnancy, from the early weeks to the trimesters, and learning how to calculate weeks into months, is crucial for expectant parents. This knowledge helps in monitoring the pregnancy’s progression, preparing for the changes that come with each stage, and ensuring the best possible care for both mother and baby. Always remember that each pregnancy is unique, and it’s essential to consult with healthcare professionals for personalized advice and care.
Disclaimer
This article provides general information about pregnancy and should not replace medical advice from a healthcare professional. Always consult with your healthcare provider for personalized guidance and care during pregnancy. The author disclaims any responsibility for any harm or consequences that may result from the use of the information presented in this article.