Did you know that approximately 70% of individuals experience facial muscle spasms at some point in their lives? These involuntary contractions can manifest in various forms, particularly as cheek twitching. Understanding the causes of cheek twitching and facial muscle spasms is crucial, as these phenomena can be exacerbated by factors such as stress, fatigue, and underlying health conditions. By examining facial muscle spasm causes, one can gain insights into effective management and treatment options for this often-misunderstood issue.
Key Takeaways
- Facial muscle spasms affect a significant portion of the population.
- Common triggers include stress and sleep deprivation.
- Medical conditions may also contribute to facial spasms.
- Understanding facial muscle spasm causes aids in treatment.
- Effective management can improve quality of life for affected individuals.
Understanding Facial Muscle Spasms
Facial muscle spasms refer to involuntary contractions that disrupt the normal functioning of facial muscles. These spasms can manifest in various ways and may often lead to confusion regarding their underlying causes. Understanding the condition involves exploring what are facial muscle spasms and recognizing their common symptoms.
What Are Facial Muscle Spasms?
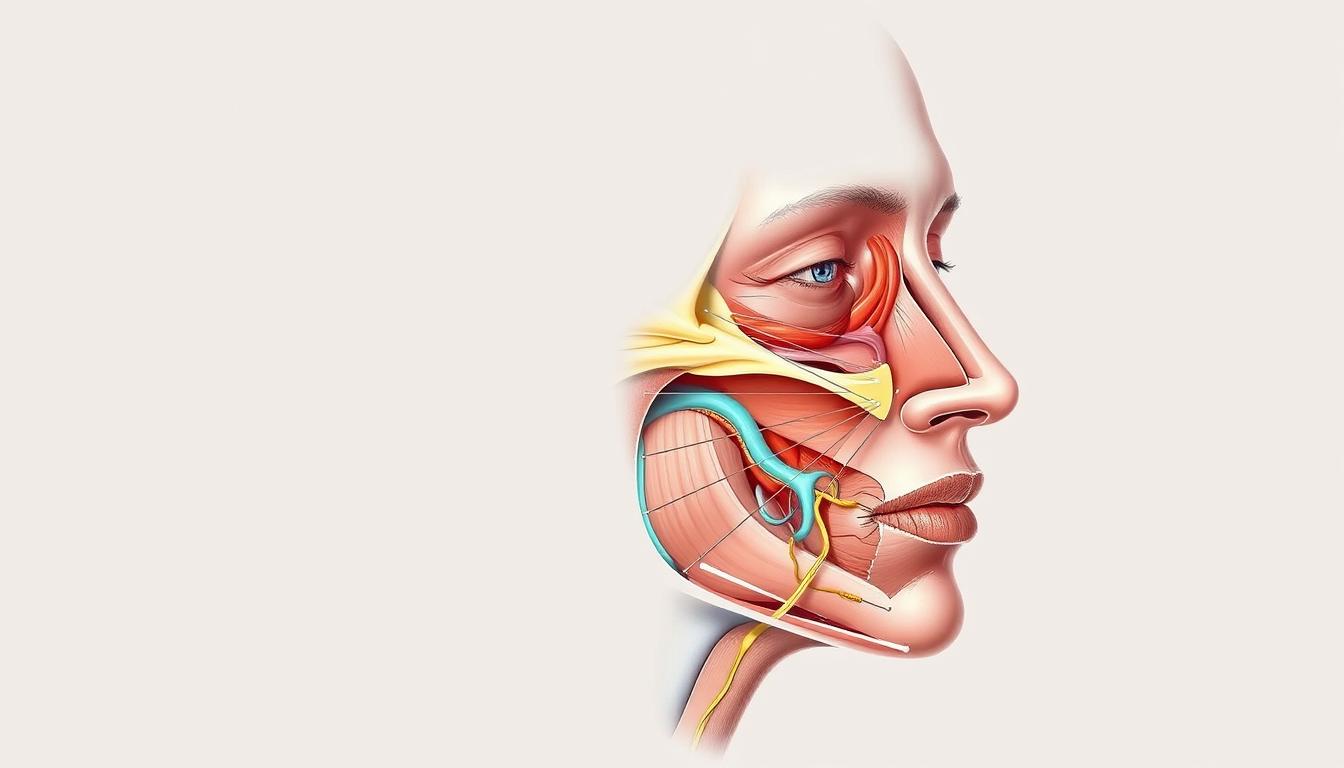
Facial muscle spasms are characterized by sudden, involuntary contractions in the facial muscles. These episodes can be brief but may occur sporadically throughout the day. A common type of facial muscle spasm is hemifacial spasm, which initially affects the eyelids and can extend to other areas of the face. This condition may mimic more serious neurological disorders, making it essential to accurately identify what are facial muscle spasms to ensure appropriate care.
Common Symptoms of Facial Spasms
The common symptoms of facial spasms include jerking movements that typically do not cause pain. Affected individuals may notice the spasms occurring in specific muscles, leading to noticeable facial movements. Symptoms can appear intermittently or persistently, and their intensity can vary. Identifying these symptoms is crucial for those experiencing them, as it aids in determining the best course of action.
Causes of Cheek Twitching and Facial Muscle Spasms
Cheek twitching and facial muscle spasms can stem from a variety of origins. Understanding these causes is essential for effective management. Various triggers and underlying medical conditions play significant roles in these occurrences.
Common Triggers
Stress, anxiety, and fatigue are among the most prevalent triggers for facial spasms and twitching. People experiencing high levels of emotional strain may notice an increase in episodes. Such instances can often occur during periods of significant physical fatigue as well. Recognizing these factors forms the basis of cheek twitching explanations and proactive measures toward reduction.
Medical Conditions Leading to Facial Spasms
Several medical conditions are linked to facial muscle spasms. Neurological disorders, such as Bell’s Palsy, are well-documented causes. This condition results from dysfunction of the facial nerve, leading to temporary facial paralysis. Hemifacial spasms, on the other hand, can appear without a clear trigger but may relate to blood vessels impinging on facial nerves. Understanding these medical conditions is crucial in identifying the reasons for cheek twitching, enabling more effective treatment strategies.
Facial Twitch Triggers
Facial twitch triggers can arise from various emotional and physical states, significantly impacting the frequency and intensity of spasms. Among these, stress and anxiety, along with fatigue and sleep deprivation, stand out as principal contributors.
Stress and Anxiety
Emotional turmoil, particularly stress and anxiety, frequently leads to facial spasms. The body’s natural response to heightened stress levels often includes involuntary muscle contractions. Psychological research indicates that prolonged exposure to stress can result in increased incidences of facial twitching. When individuals experience high levels of anxiety, these facial twitch triggers become more pronounced, resulting in noticeable discomfort.
Fatigue and Sleep Deprivation
Physical conditions like fatigue and sleep deprivation play a critical role in aggravating muscle responses. Insufficient sleep often leads to exhaustion, making the muscles more susceptible to involuntary movements. Studies suggest that the relationship between fatigue and increased facial spasms is significant, highlighting a need for adequate rest. By addressing issues related to fatigue and sleep deprivation, individuals can reduce the likelihood of experiencing painful and distracting muscle twitches.
Muscle Spasm in Face Factors
Understanding the various muscle spasm in face factors is essential for recognizing underlying health concerns. Neurological disorders often play a significant role in the onset of these spasms, disrupting the normal functioning of nerve pathways and potentially triggering involuntary muscle contractions. In addition to neurological issues, various injuries and tumors can contribute to facial twitching and spasms, further complicating diagnosis and treatment.
Neurological Disorders
A range of neurological disorders can lead to facial muscle spasms. Conditions such as multiple sclerosis, Parkinson’s disease, and Bell’s palsy can interfere with nerve signaling, causing involuntary movements. Hemifacial spasm particularly exemplifies the impact of neurological factors, where abnormalities related to blood vessel placement near the facial nerve lead to erratic muscle contractions. Such disorders require careful evaluation to differentiate between benign and more severe causes of facial spasms.
Injuries and Tumors
Injuries and tumors constitute another critical aspect of muscle spasm in face factors. Trauma to the head or neck may result in nerve damage, posing risks for involuntary facial movements. Tumors, especially those located behind the ear, can impinge on facial nerves, triggering spasms. Identifying these conditions is vital as they often necessitate different treatment approaches compared to those associated with purely neurological disorders.
What Causes Facial Muscle Spasms?
Facial muscle spasms can arise from various factors impacting nerve function and muscle control. Understanding what causes facial muscle spasms offers insight into effective management and treatment options.
Blood Vessel Interference
One significant contributor to facial muscle spasms is blood vessel interference. This condition often manifests in hemifacial spasm, where blood vessels exert pressure on facial nerves. The consequent irritation can trigger chronic spasms, typically beginning near the eyelid. Over time, these spasms may progress, affecting broader areas of the face. Identifying and addressing blood vessel interference is crucial for alleviating these symptoms and may involve medical interventions.
Secondary Causes of Hemifacial Spasms
Several secondary causes of hemifacial spasms need consideration. Conditions such as Bell’s Palsy represent one potential complication that can impact facial nerve health. Infections affecting the facial nerves or various neurological disorders may also contribute to the development of hemifacial spasms. An in-depth exploration of these secondary causes of hemifacial spasms informs clinicians regarding suitable treatment strategies, as underlying health conditions significantly shape therapeutic approaches.
| Cause | Description |
|---|---|
| Blood Vessel Interference | Pressure from blood vessels causing chronic facial spasms. |
| Bells’s Palsy | A condition impacting nerve function that may result in spasms. |
| Neurological Disorders | Various disorders can affect nerve health, leading to spasms. |
| Infections | Infections can contribute to nerve damage and spasms. |
Treatment Options for Facial Spasms
Treatment options for facial spasms can encompass a wide range of approaches, from over-the-counter remedies to more invasive medical treatments and procedures. Understanding these options is crucial for managing symptoms effectively.
Over-the-Counter Remedies
Over-the-counter remedies often provide initial relief for individuals experiencing mild facial spasms. Common choices include muscle relaxants and mild sedatives that target symptoms caused by stress or fatigue. These products can help alleviate tension and promote relaxation, making them an accessible option for many.
Medical Treatments and Procedures
For more severe cases, medical treatments and procedures become necessary. One effective intervention includes botulinum toxin injections, which have demonstrated notable success in reducing symptoms, particularly in cases of hemifacial spasm. In situations where nerve pressure is a significant concern, surgical approaches such as microvascular decompression may be warranted. These comprehensive treatment strategies aim to enhance the overall quality of life for patients dealing with facial spasms.
Conclusion
Understanding the facial muscle spasm origins is crucial for those experiencing cheek twitching and facial muscle spasms. These spasms can stem from a variety of factors, both emotional and physical, which highlights the need for comprehensive evaluation and treatment planning. By identifying specific triggers such as stress, fatigue, or more serious neurological conditions, individuals can approach their symptoms with greater awareness and control.
Additionally, awareness of the diverse facial muscle spasm causes sheds light on the necessity of timely medical intervention. With ongoing research and advancements in treatment options, there is a growing potential to improve outcomes for those affected by these conditions. Knowledge about effective remedies, both OTC and medical procedures, empowers patients to take proactive steps towards relief.
Ultimately, education plays a pivotal role in improving the quality of life for individuals facing facial muscle spasms. By grasping the complexities of what contributes to these spasms, affected individuals can engage in discussions with healthcare providers and explore personalized treatment pathways designed to suit their unique needs.